Understanding Calibration Out of Tolerance (OOT) and How CalWeb Helps You Stay in Control

In the world of test and measurement, precision is everything. Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, electronics, or manufacturing, the accuracy of your instruments directly impacts product quality, safety, and compliance. One critical concept in calibration that often raises questions is "Out of Tolerance" (OOT). What does it mean, why does it matter, and how can you manage it effectively? Let’s break it down.
What Is "Out of Tolerance" (OOT)?
When a piece of test equipment is calibrated, its performance is compared against a known standard. If any measurement point on the device falls outside the manufacturer’s specified limits or the user-defined tolerance range, it is considered Out of Tolerance (OOT).
These limits may be:
- Manufacturer-specified: Based on the original design and performance specifications.
- User-defined: Customized based on internal quality requirements or specific application needs. In regulated environments, user-defined tolerances should be justified with documented risk assessments and validated against process requirements.
For example, if a digital multimeter is supposed to measure 5.000 V ± 0.005 V, and it reads 5.010 V, it is OOT. This deviation, even if seemingly small, can have significant consequences depending on the application.
The Role of Measurement Uncertainty and Decision Rules
OOT decisions are not made in isolation. Every calibration measurement includes an associated measurement uncertainty, which quantifies the confidence in the result. If the measured value plus its uncertainty overlaps the tolerance limit, the result may be considered borderline or inconclusive, depending on your organization's decision rule.
A decision rule defines how measurement uncertainty is considered when determining whether a result is in or out of tolerance. This is a key requirement under ISO/IEC 17025:2017.
Tektronix Decision Rules: A Practical Example
Tektronix offers several decision rules to accommodate different customer needs:
- Decision Rule 0 – Data Only: Measurement results are reported without a pass/fail determination. Only the measured value and its uncertainty are provided. This is useful when customers want to make their own conformity decisions.
- Decision Rule 1 – Simple Acceptance: The measured value must fall within the specified tolerance limits. Uncertainty is reported but not used to adjust the limits. This rule aligns with ILAC-G8:09/2019 and is commonly used when the Test Uncertainty Ratio (TUR) is greater than 4:1.
- Decision Rule 2 – Guard Banding: Tolerance limits are reduced by the measurement uncertainty to create a more conservative acceptance zone. If the result falls within this tighter band, it is considered in-tolerance. If it falls outside the guard band but within the original tolerance, the result is labeled Pass* or Fail*—indicating an indeterminate status that requires customer review.
These rules help ensure that calibration results are interpreted consistently and transparently, especially in regulated environments. Tektronix customers can select the rule that best fits their risk tolerance and compliance requirements.
Why Does OOT Matter?
An OOT condition can indicate that your equipment has been providing inaccurate readings—possibly for an extended period. This can lead to:
- Product defects due to incorrect measurements
- Safety risks in critical systems
- Regulatory non-compliance, especially in industries governed by standards like ISO/IEC 17025, FDA, or FAA
- Costly rework or recalls if faulty products have already been shipped
OOT Severity: Not All OOTs Are Equal
Experienced quality professionals know that not every OOT has the same impact. It’s important to classify OOT events based on severity:
- Minor: Slight deviation with no impact on product quality or safety
- Moderate: Potential impact requiring limited rework or review
- Critical: High risk to safety, compliance, or product integrity
This classification helps prioritize corrective actions and resource allocation.
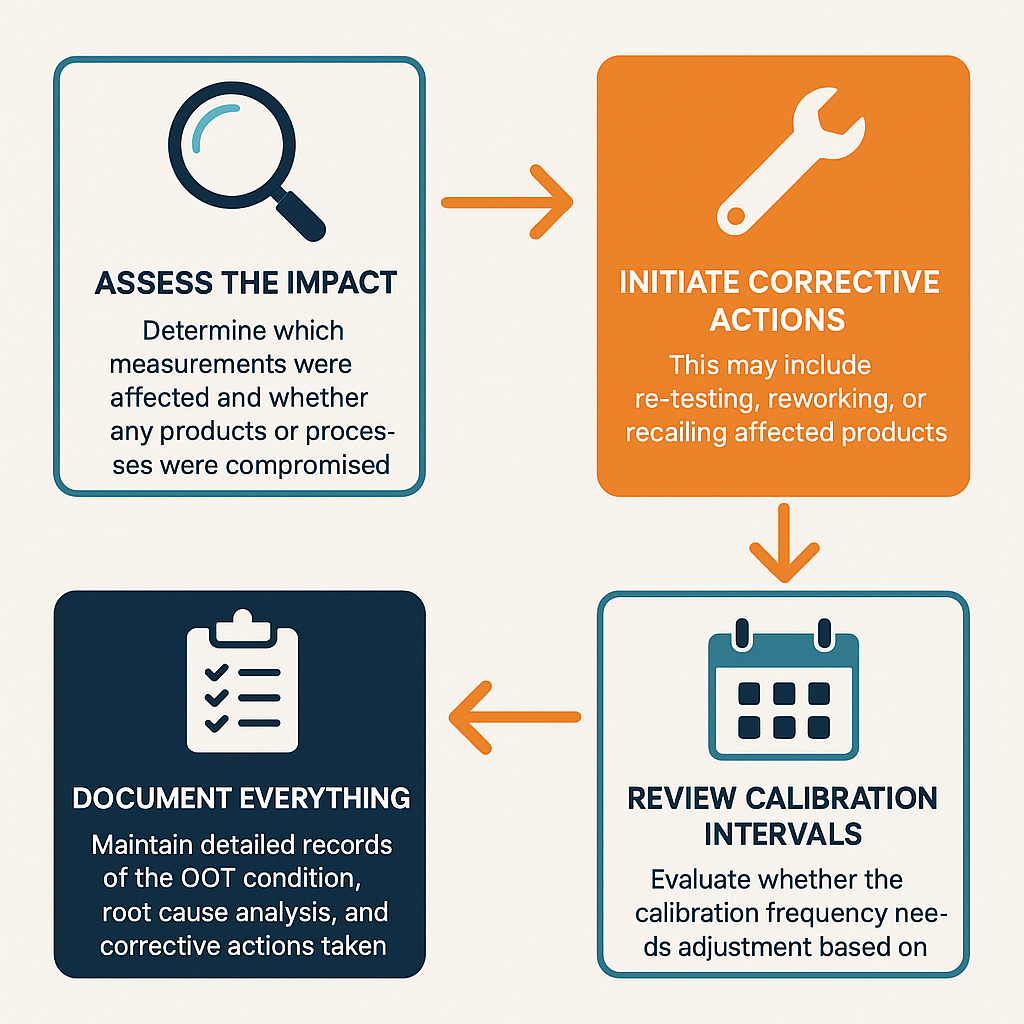
What Should You Do When Equipment Is OOT?
When a calibration reveals an OOT condition, you should:
- Assess the impact: Determine what measurements were affected and whether any products or processes were compromised.
- Initiate corrective actions: This may include re-testing, reworking, or even recalling affected products.
- Review calibration intervals: An OOT result might indicate that your calibration frequency needs adjustment.
- Document everything: Maintain detailed records of the OOT condition, root cause analysis, corrective actions taken, and review of the calibration interval
Why Is OOT Management Required?
Proper OOT management is not just good practice—it’s often a regulatory requirement. Standards like ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 17025 mandate that organizations have procedures in place to handle OOT conditions. Effective OOT management ensures:
- Traceability of measurement data
- Accountability for quality assurance
- Audit readiness for internal and external reviews
- Continuous improvement in measurement reliability
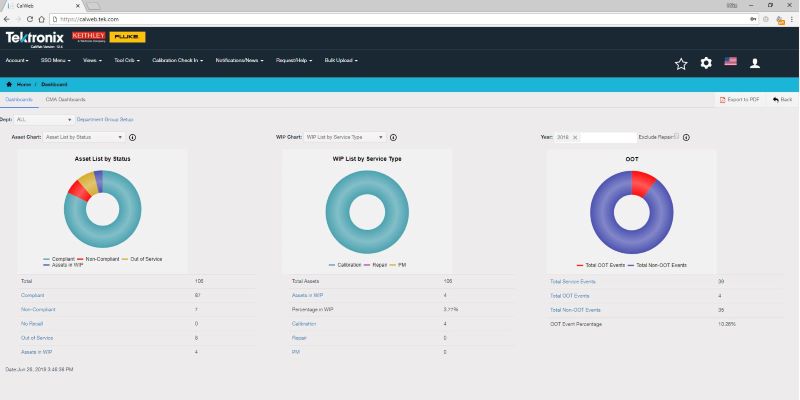
How CalWeb Helps You Manage OOT Efficiently
Tektronix’s CalWeb Calibration Management SaaS application is designed to simplify and streamline the entire calibration lifecycle—including OOT management. Here’s how:
- Real-Time OOT Alerts: Instantly notifies you when an instrument is found OOT during calibration.
- Compliance Support: Ensures your OOT handling aligns with industry standards and audit requirements.
- OOT Case Management: Track OOT events and documentation as you investigate them to resolution.
Final Thoughts
OOT conditions are inevitable in any calibration program—but how you manage them makes all the difference. With CalWeb, you gain the visibility, control, and confidence needed to handle OOT events proactively and compliantly. It’s not just about fixing problems—it’s about preventing them.
Ready to take control of your calibration program? Learn more about how CalWeb can transform your OOT management strategy.


